publications
Publications by categories in reversed chronological order. generated by jekyll-scholar.
2026
-
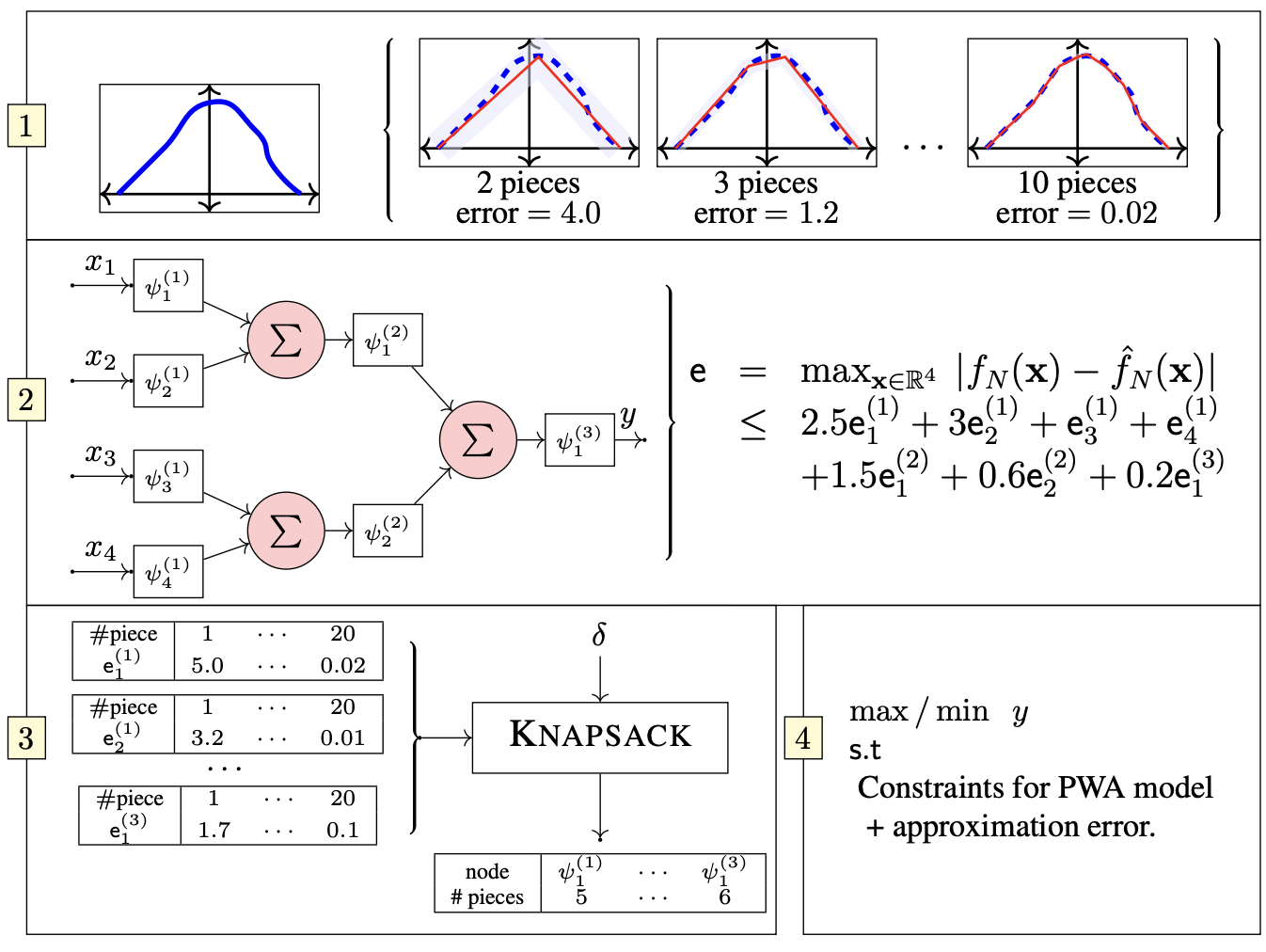 Optimal Abstractions for Verifying Properties of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs)Noah Schwartz*, Chandra Kanth Nagesh*, Sriram Sankaranarayanan, and 3 more authorsFeb 2026Preprint
Optimal Abstractions for Verifying Properties of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs)Noah Schwartz*, Chandra Kanth Nagesh*, Sriram Sankaranarayanan, and 3 more authorsFeb 2026PreprintWe present a novel approach for verifying properties of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs), a class of neural networks characterized by nonlinear, univariate activation functions typically implemented as piecewise polynomial splines or Gaussian processes. Our method creates mathematical “abstractions” by replacing each KAN unit with a piecewise affine (PWA) function, providing both local and global error estimates between the original network and its approximation. These abstractions enable property verification by encoding the problem as a Mixed Integer Linear Program (MILP), determining whether outputs satisfy specified properties when inputs belong to a given set. A critical challenge lies in balancing the number of pieces in the PWA approximation: too many pieces add binary variables that make verification computationally intractable, while too few pieces create excessive error margins that yield uninformative bounds. Our key contribution is a systematic framework that exploits KAN structure to find optimal abstractions. By combining dynamic programming at the unit level with a knapsack optimization across the network, we minimize the total number of pieces while guaranteeing specified error bounds. This approach determines the optimal approximation strategy for each unit while maintaining overall accuracy requirements. Empirical evaluation across multiple KAN benchmarks demonstrates that the upfront analysis costs of our method are justified by superior verification results.
title = {Optimal Abstractions for Verifying Properties of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs)}, author = {Schwartz*, Noah and Nagesh*, Chandra Kanth and Sankaranarayanan, Sriram and Kaur, Ramneet and Sahai, Tuhin and Jha, Susmit}, year = {2026}, month = feb, note = {Preprint}, eprint = {2602.06737}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.LG}, }
2025
-
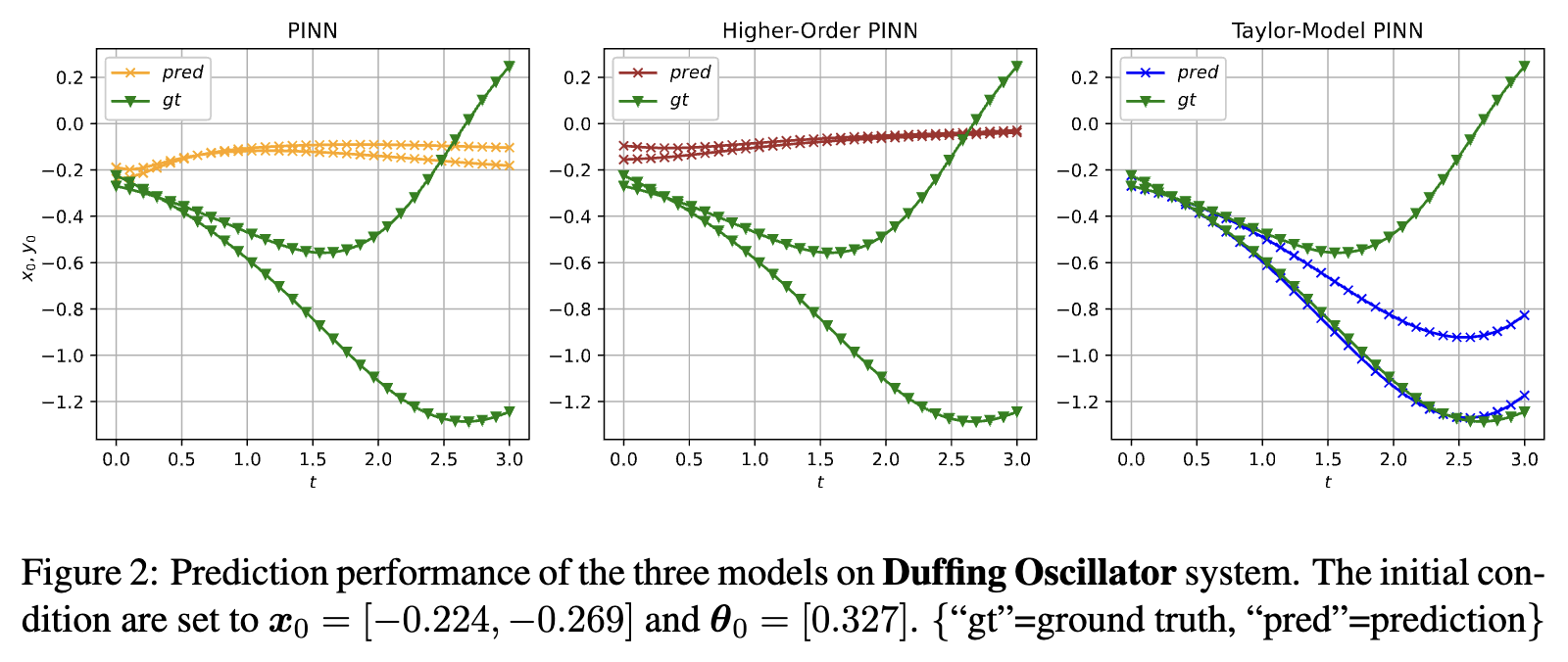 Taylor-Model Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) for Ordinary Differential EquationsChandra Kanth Nagesh, Sriram Sankaranarayanan, Ramneet Kaur, and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the International Conference on Neuro-symbolic Systems (NeuS), May 2025
Taylor-Model Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) for Ordinary Differential EquationsChandra Kanth Nagesh, Sriram Sankaranarayanan, Ramneet Kaur, and 2 more authorsIn Proceedings of the International Conference on Neuro-symbolic Systems (NeuS), May 2025We study the problem of learning neural network models for Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) with parametric uncertainties. Such neural network models capture the solution to the ODE over a given set of parameters, initial conditions, and range of times. Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) have emerged as a promising approach for learning such models that combine data-driven deep learning with symbolic physics models in a principled manner. However, the accuracy of PINNs degrade when they are used to solve an entire family of initial value problems characterized by varying parameters and initial conditions. In this paper, we combine symbolic differentiation and Taylor series methods to propose a class of higher-order models for capturing the solutions to ODEs. These models combine neural networks and symbolic terms: they use higher order Lie derivatives and a Taylor series expansion obtained symbolically, with the remainder term modeled as a neural network. The key insight is that the remainder term can itself be modeled as a solution to a first-order ODE. We show how the use of these higher order PINNs can improve accuracy using interesting, but challenging ODE benchmarks. We also show that the resulting model can be quite useful for situations such as controlling uncertain physical systems modeled as ODEs.
@inproceedings{pmlr-v288-nagesh25a, title = {Taylor-Model Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) for Ordinary Differential Equations}, author = {Nagesh, Chandra Kanth and Sankaranarayanan, Sriram and Kaur, Ramneet and Sahai, Tuhin and Jha, Susmit}, year = {2025}, month = may, booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on Neuro-symbolic Systems (NeuS)}, publisher = {PMLR}, series = {Proceedings of Machine Learning Research}, volume = {288}, pages = {621--642}, editor = {Pappas, George and Ravikumar, Pradeep and Seshia, Sanjit A.}, }
2024
-
 Salient Object Detection for Images Taken by People With Vision ImpairmentsChandra Kanth Nagesh*, Jarek Reynolds*, and Danna GurariIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Jan 2024
Salient Object Detection for Images Taken by People With Vision ImpairmentsChandra Kanth Nagesh*, Jarek Reynolds*, and Danna GurariIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Jan 2024Salient object detection is the task of producing a binary mask for an image that deciphers which pixels belong to the foreground object versus background. We introduce a new salient object detection dataset using images taken by people who are visually impaired who were seeking to better understand their surroundings, which we call VizWiz-SalientObject. Compared to seven existing datasets, VizWiz-SalientObject is the largest (i.e., 32,000 human-annotated images) and contains unique characteristics including a higher prevalence of text in the salient objects (i.e., in 68% of images) and salient objects that occupy a larger ratio of the images (i.e., on average, 50% coverage). We benchmarked seven modern salient object detection methods on our dataset and found they struggle most with images featuring salient objects that are large, have less complex boundaries, and lack text as well as for lower quality images. We invite the broader community to work on our new dataset challenge by publicly sharing the dataset at this https https://vizwiz.org/tasks-and-datasets/salient-object.
@inproceedings{Nagesh_Reynolds_2024_WACV, title = {Salient Object Detection for Images Taken by People With Vision Impairments}, author = {Nagesh*, Chandra Kanth and Reynolds*, Jarek and Gurari, Danna}, year = {2024}, month = jan, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)}, pages = {8522--8531}, }
2022
-
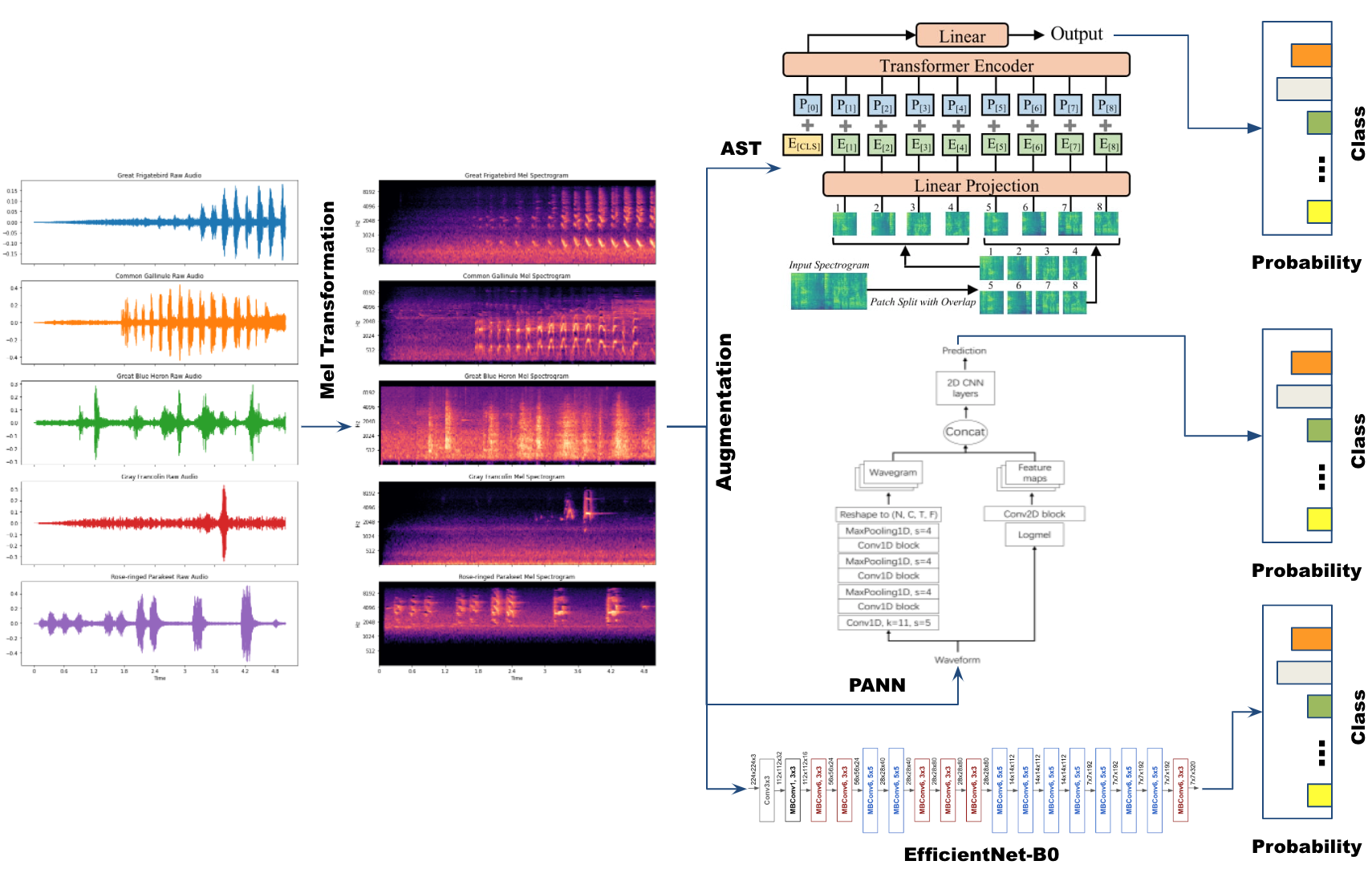 The Birds Need Attention Too: Analysing usage of Self Attention in identifying bird calls in soundscapesChandra Kanth Nagesh, and Abhishek PurushothamaJan 2022
The Birds Need Attention Too: Analysing usage of Self Attention in identifying bird calls in soundscapesChandra Kanth Nagesh, and Abhishek PurushothamaJan 2022Birds are vital parts of ecosystems across the world and are an excellent measure of the quality of life on earth. Many bird species are endangered while others are already extinct. Ecological efforts in understanding and monitoring bird populations are important to conserve their habitat and species, but this mostly relies on manual methods in rough terrains. Recent advances in Machine Learning and Deep Learning have made automatic bird recognition in diverse environments possible. Birdcall recognition till now has been performed using convolutional neural networks. In this work, we try and understand how self-attention can aid in this endeavor. With that we build an pre-trained Attention-based Spectrogram Transformer baseline for BirdCLEF 2022 and compare the results against the pre-trained Convolution-based baseline. Our results show that the transformer models outperformed the convolutional model and we further validate our results by building baselines and analyzing the results for the previous year BirdCLEF 2021 challenge. Source code available at this https://github.com/ck090/BirdCLEF-22
@misc{nagesh2022birds, title = {The Birds Need Attention Too: Analysing usage of Self Attention in identifying bird calls in soundscapes}, author = {Nagesh, Chandra Kanth and Purushothama, Abhishek}, year = {2022}, eprint = {2211.07722}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.MM}, }
2019
-
 Identifying Missing Component in the Bechdel Test Using Principal Component Analysis MethodChandra Kanth Nagesh, Raghav Lakhotia, and Krishna MadgulaIn Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Jan 2019
Identifying Missing Component in the Bechdel Test Using Principal Component Analysis MethodChandra Kanth Nagesh, Raghav Lakhotia, and Krishna MadgulaIn Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Jan 2019A lot has been said and discussed regarding the rationale and significance of the Bechdel Score. It became a digital sensation in 2013 when Swedish cinemas began to showcase the Bechdel test score of a film alongside its rating. The test has drawn criticism from experts and the film fraternity regarding its use to rate the female presence in a movie. The pundits believe that the score is too simplified and the underlying criteria of a film to pass the test must include 1) at least two women, 2) who have at least one dialogue, 3) about something other than a man, is egregious. In this research, we have considered a few more parameters which highlight how we represent females in film, like the number of female dialogues in a movie, dialogue genre, and part of speech tags in the dialogue. The parameters were missing in the existing criteria to calculate the Bechdel score. The research aims to analyze 342 movies scripts to test a hypothesis if these extra parameters, above with the current Bechdel criteria, are significant in calculating the female representation score. The result of the Principal Component Analysis method concludes that the female dialogue content is a key component and should be considered while measuring the representation of women in a work of fiction.
@inproceedings{lakhotia2019identifying, title = {Identifying Missing Component in the Bechdel Test Using Principal Component Analysis Method}, author = {Nagesh, Chandra Kanth and Lakhotia, Raghav and Madgula, Krishna}, year = {2019}, booktitle = {Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA)}, }
2017
-
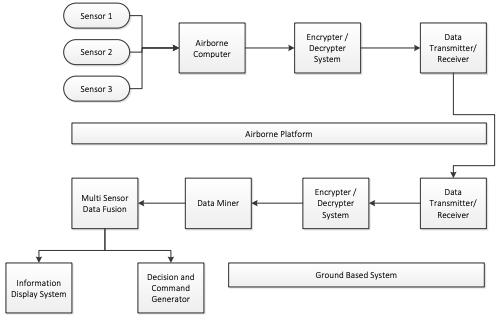 Secure Handshake Mechanism for Autonomous Flying Agents Using Robust CryptosystemChandra Kanth Nagesh, KN Rao, and Anjan K KoundinyaIn Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solution (CSITSS), Jan 2017
Secure Handshake Mechanism for Autonomous Flying Agents Using Robust CryptosystemChandra Kanth Nagesh, KN Rao, and Anjan K KoundinyaIn Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solution (CSITSS), Jan 2017The autonomous flying agents in a Network-centric environment and brings out various security threats and various techniques of Cryptography. Primary Focus is on study and implementation of how cryptographic algorithms can be effectively be used in a warfare scenario. The data security is the utmost key factor for the protection of data in such environments. The paper proposes mechanisms secured data transmission from the command center (which can be the sending flying agent) to shooter target. The command center and shooter target have a unique set of encryption and decryption key which are created randomly by calibrating the security level at run time. In the beginning, the encryption key used for encrypting data is received from a shooter target when the communication is authenticated through UDP sockets. The encrypted data is sent to the shooter target with the signed signature and command center’s encryption key. The encrypted data and signature are then decrypted and verified respectively at the shooter target. The time analysis is performed and observed inputs are provided to the command center.
@inproceedings{nagesh2019secure, title = {Secure Handshake Mechanism for Autonomous Flying Agents Using Robust Cryptosystem}, author = {Nagesh, Chandra Kanth and Rao, KN and Koundinya, Anjan K}, year = {2017}, journal = {Proceedings of International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solution (CSITSS)}, booktitle = {Proceedings of 2nd International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solution (CSITSS)}, }